In this week’s #AskTheAgronomist, Precision Agronomy Advisor Phil Long discusses Pivot Bio’s ProveN product and how it can enhance your yield results.
For more agronomy videos, check out our Latham Seeds YouTube Channel.

In this week’s #AskTheAgronomist, Precision Agronomy Advisor Phil Long discusses Pivot Bio’s ProveN product and how it can enhance your yield results.
For more agronomy videos, check out our Latham Seeds YouTube Channel.

After enjoying a career that spanned more than 25 years with Latham Hi‑Tech Seeds, Mark Grundmeier plans to box up his office on December 17, 2021, and then pack his bags for the holidays. He and his wife, Jerri, are ready to hit the road! They’re planning to see more of the United States as they travel around to visit family members and friends.

Mark and Jerri look forward to spending more time with their children and grandchildren. Their son, Craig, graduated from Drake University in 2003. He works as an Executive Benefits Administrator for Principal Financial Group in Des Moines. Craig and his wife, Lauren, live in Urbandale with their two children, Liam and Ava. Lauren works as a Clinical Dietitian at Unity Point Health in Des Moines.
Mark and Jerri’s oldest daughter, Krystal, graduated from Waldorf University in 2006. She works as a guidance counselor at an elementary school in the Dallas area. She and her husband, Michael, have three children: Kennedy, Kelsie and Kason. Michael is a senior consultant/program manager for the D&M Enterprise Group. The Grundmeier’s daughter Stacie graduated in 2010 from Iowa State University (ISU). She also lives in the Dallas area where she works as Business Development Director for Haggar Clothing.

Youngest daughter, Kaitlan, started at North Iowa Area Community College (NIACC) and then transferred to ISU. She works as a loan processor for a bank in Missouri. Her husband, Paul, works as a heavy equipment operator for the City of St. Roberts.
“Our grandchildren are getting to that age where they’re getting involved in sports and other activities, so we’re looking forward to having the time to attend more of my grandchildren’s activities,” says Mark. He also plans to spend more time during the summer months, enjoying his hobbies of fishing, golfing and gardening. His hobbies and interests certainly influenced his career path.
After earning a bachelor’s degree in Fisheries and Wildlife Biology (FWB) from Iowa State University, Mark worked part time for Farm Service Co-op. He desired to work in FWB, so Mark then accepted a summer internship with the Central Platte Natural Resource District (NRD) in Grand Island, Nebraska. He met with farmers throughout the region, helping them develop and implement wildlife management plans. Mark was offered two, full-time NRD jobs at the summer’s end. However, the positions paid less than minimum wage. He was months away from getting married and needed a better job, so when his former boss at the co-op contacted him about a management trainee position, he gladly accepted.
“As God has been with me my whole life, He was also with me then,” says Mark. “The co-op manager that I had worked for earlier that year called me to say they were looking for somebody to start in the Farm Service Co-op system as a Management Trainee. The starting wage was almost twice what the NRD had offered me!”
That phone call led Mark to a 19-year career at Farm Service Co-op where he worked up through the ranks. One day he was reading his mail and saw in a newsletter that John Holmes was leaving Latham Seeds, and Mark said that was his chance at a “dream job.” Mark joined the Latham Team in October 1996.
“What I have enjoyed most about working at Latham Seeds is the opportunity to get into research and learn from Bill Latham. The family atmosphere has been one of the outstanding things about Latham Seeds,” says Mark. “I feel as though the Latham family – employees, dealers and customers – are part of my extended family. While I’m ready to retire, I’ll really miss the close association with the people I’ve come to know over the past 25+ years of being here.”
We certainly wish Mark all the best in his retirement! I know I speak on behalf of the entire Latham Team when I say we will miss Mark’s can-do, positive attitude and seeing his smiling face in our hallways. Fortunately, Mark and Jerri live near the Latham Seeds office. We certainly hope they’ll stop in from time to time, and continue to join us for annual events like our company’s annual Cy-Hawk Tailgate and Christmas potluck.
Tailgates and holidays wouldn’t be complete without loads of meat! Mark enjoys smoking a whole pork shoulder or loin. After he and Jerri enjoy the first meal, the leftovers are turned into casseroles, sandwiches or wraps. They recently discovered an Instant Pot recipe that they’re sharing with us today.

As we were conducting our pre-harvest field inspections, many production growers said they’d be happy with 40-bushel yields due to the early cold spell followed by drought. I’m happy to report that most of our growers’ yields were in the mid-50s to the mid-60s, and some even saw yields of 70 bushels per acre (bu/A) or more!
It seems that a few timely rains in August made the difference between having a decent crop and having a poor one. Below are raw yield results from some soybean Latham® Showcase plots and Latham Elite trials harvested this fall:

Keep checking lathamseeds.com for updated yield results from plots around Latham Country.
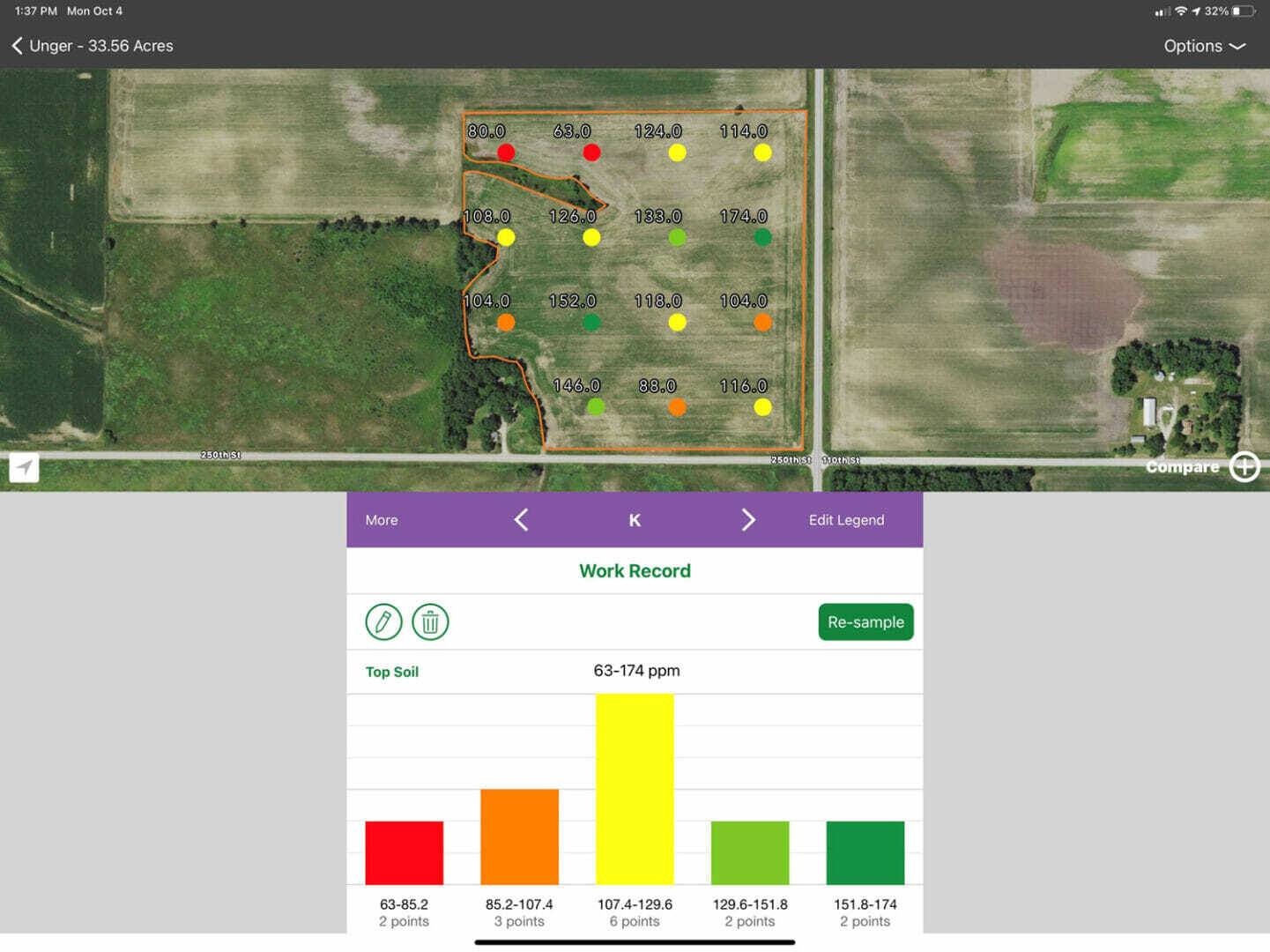
You could lose more than you save if you cut costs in the wrong places.
Some farmers are thinking about cutting back on their fertility program for 2022 crops because fertilizer costs are increasing and pre-order prices aren’t guaranteed into next spring. I understand that price hikes cause uncertainty. As someone who also farms, I feel the same way. What I’ve learned is that fertility is the foundation to keeping a crop healthy all season. Top-performing hybrids need food to fuel their growth.
Below are three questions to ask yourself as you plan your 2022 fertility program:
Remember, every 100 pounds of nitrogen applied requires about 500 pounds of lime to offset the acidity created by the nitrogen conversion process. Make sure your pH is correct, so all the nutrients in your soil are available to your growing crop. Correct soil pH before you try to build your P, K or micronutrients.
Feel free to call me if you have any questions about how Data Forward can help you collect and store information that can lead to more profitable farm management decisions.

“Repetition is effective. Repetition is effective.” – Legendary Broadcaster Paul Harvey
The massive amounts of information we process each day makes it easy for messages to get diluted or forgotten. That’s why I find it helpful to continually review the basics, especially when it comes to feeding corn silage.
What gets fed to dairy cattle, as well as to beef cattle, affects the quality and quantity of the milk and meat produced. We know there is a correlation between starch and fiber digestibility with rates of gain. Getting the most tonnage and high nutritional concentration gives you the best chance of improving milk quality and production in dairy, as well as rates of gains in beef.
Most of the silage research to date deals with feeding corn silage to dairy cattle. However, Iowa State University has updated its Beef Corn Silage Calculator that ranks the potential value of corn silage varieties used in beef rations.
You also get an index ranking for Latham® hybrids in our seed guide. Our index rating shows a hybrid trend on a multi-season, multi-environment basis. Keep in mind that management practices, weather, and fertility can dramatically impact forage quality.
Simply stated, here’s what we want from corn silage: high tonnage in the field and high quality in the bunk. Listed below are some basic corn silage terms to provide a better understanding of corn silage yield and quality:
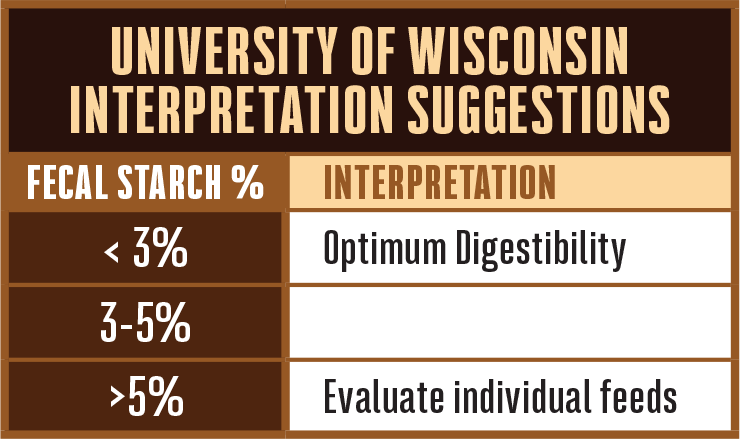 Starch Digestibility. Increasing starch digestibility supports rumen bacteria and increases energy supply to dairy and beef cows. It’s estimated that for every 1 percent of fecal starch that passes into the manure, milk production is reduced by 0.72 pounds per head per day. This adds up!
Starch Digestibility. Increasing starch digestibility supports rumen bacteria and increases energy supply to dairy and beef cows. It’s estimated that for every 1 percent of fecal starch that passes into the manure, milk production is reduced by 0.72 pounds per head per day. This adds up!There is an ocean of information available from seed guides to feed reports. Ultimately, it comes down to considering the end use first. Match your end use goals with product features and proper placement for maximum ROI at the bunk.
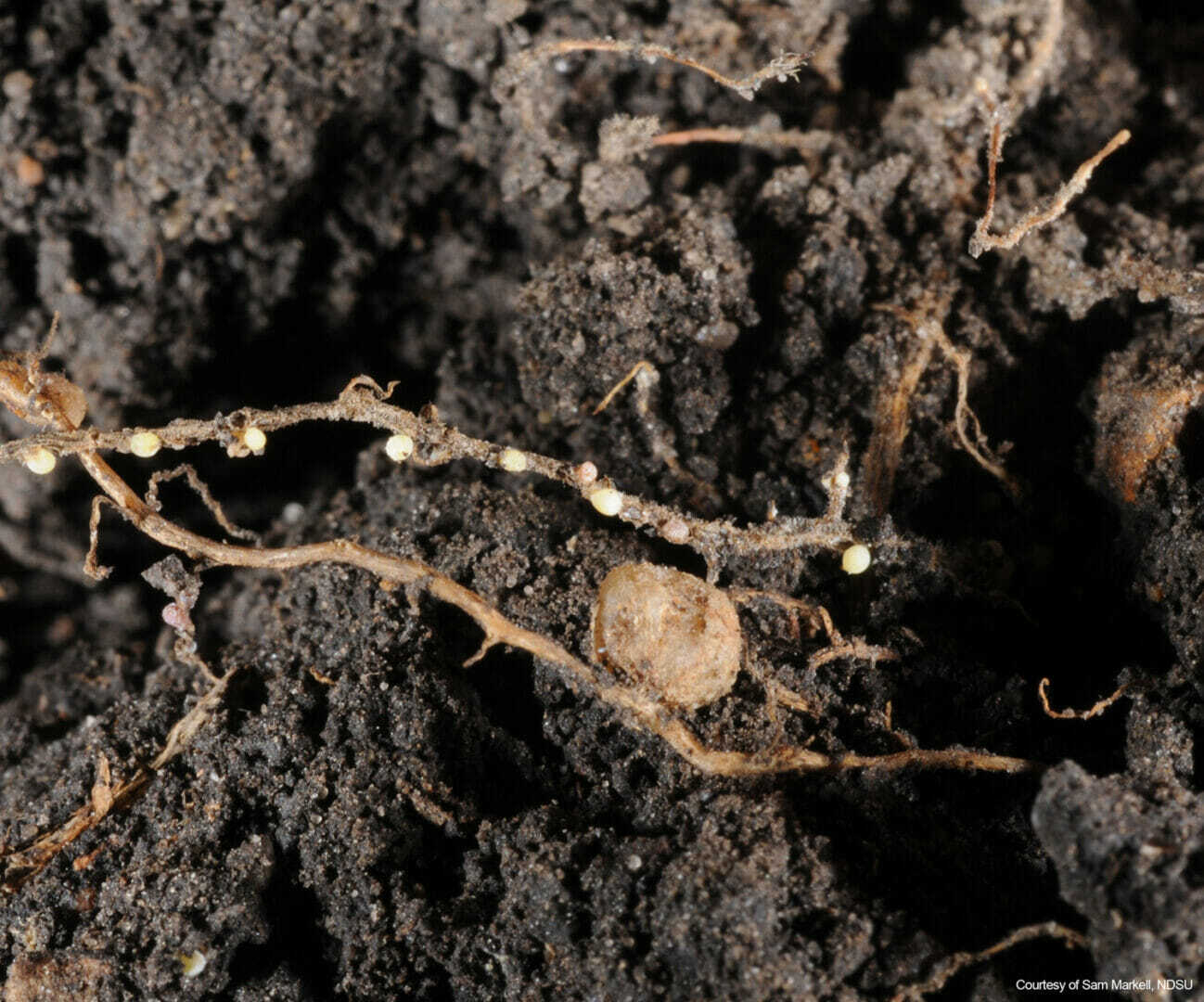
 By robbing farmers of more than 100 million bushels annually, Soybean Cyst Nematode (SCN) is estimated to be the #1 yield-robbing soybean pest or disease in the United States. Farmers may scream over lost yield this fall, but SCN is considered a “silent yield robber” due to a lack of above-ground symptoms in most fields.
By robbing farmers of more than 100 million bushels annually, Soybean Cyst Nematode (SCN) is estimated to be the #1 yield-robbing soybean pest or disease in the United States. Farmers may scream over lost yield this fall, but SCN is considered a “silent yield robber” due to a lack of above-ground symptoms in most fields.
Immediately after harvest is the best time to take soil samples for SCN. Several universities have programs that offer free soil samples to evaluate SCN, so check with your local Extension office to see if you qualify.
Think SCN isn’t a problem in your fields? Think again! Dry soil conditions, especially early in the growing season, can greatly increase the effects of SCN infestations. I received numerous calls in June and July about yellow, stunted soybeans. Most farmers suspected Iron Deficiency Chlorosis. Upon further inspection, SCN was almost always present and in larger numbers than previously observed. When I asked whether these farmers had taken a recent soil sample for SCN, most had not. They admit to mostly relying on SCN-resistant varieties to control or minimize the losses from this pest.
We have known for years that PI 88788 is gradually losing its efficacy against the pest, and more than 95% of SCN-resistant soybeans in America have PI 88788 as the source of gene resistance. Since 1997, a team of researchers at Iowa State University led by Dr. Greg Tylka has conducted annual in-field trials with hundreds of SCN-resistant varieties. They measure agronomic performance and SCN population densities from planting until after harvest.
Scientists have determined that to be effective, SCN-resistant varieties must maintain less than a 10% reproduction rate of SCN during the growing season. Since 2004, Dr. Tylka and his team have noticed that the average of all PI 88788 varieties in their trials have gradually exceeded that threshold. They have also noted that the average yield of those varieties has decreased as the SCN reproduction has increased. For more information on these studies, visit www.isuscntrials.info. Other land-grant university researchers have reported similar findings.
To effectively manage SCN in the future, soybean breeders are focusing on other sources of gene resistance. Your Latham Soybean Product Team is continually evaluating and searching for opportunities to bring new, better resistant varieties to our lineup. We also are evaluating several seed treatments for battling this pest. Saltro®, our seed treatment product for SDS protection, is also noted to have activity against SCN. More information from our Latham Elite trials will be available post-harvest.
“TAKE THE TEST. BEAT THE PEST.” is a slogan/campaign by The SCN Coalition™ and funded by the Soybean Checkoff and is designed specifically to promote awareness of SCN. These microscopic roundworms, which infect the roots of soybeans and other plants, can be present in a field for years before above-ground symptoms are visible. We encourage you to take the test this season, so you can plan accordingly for the future.
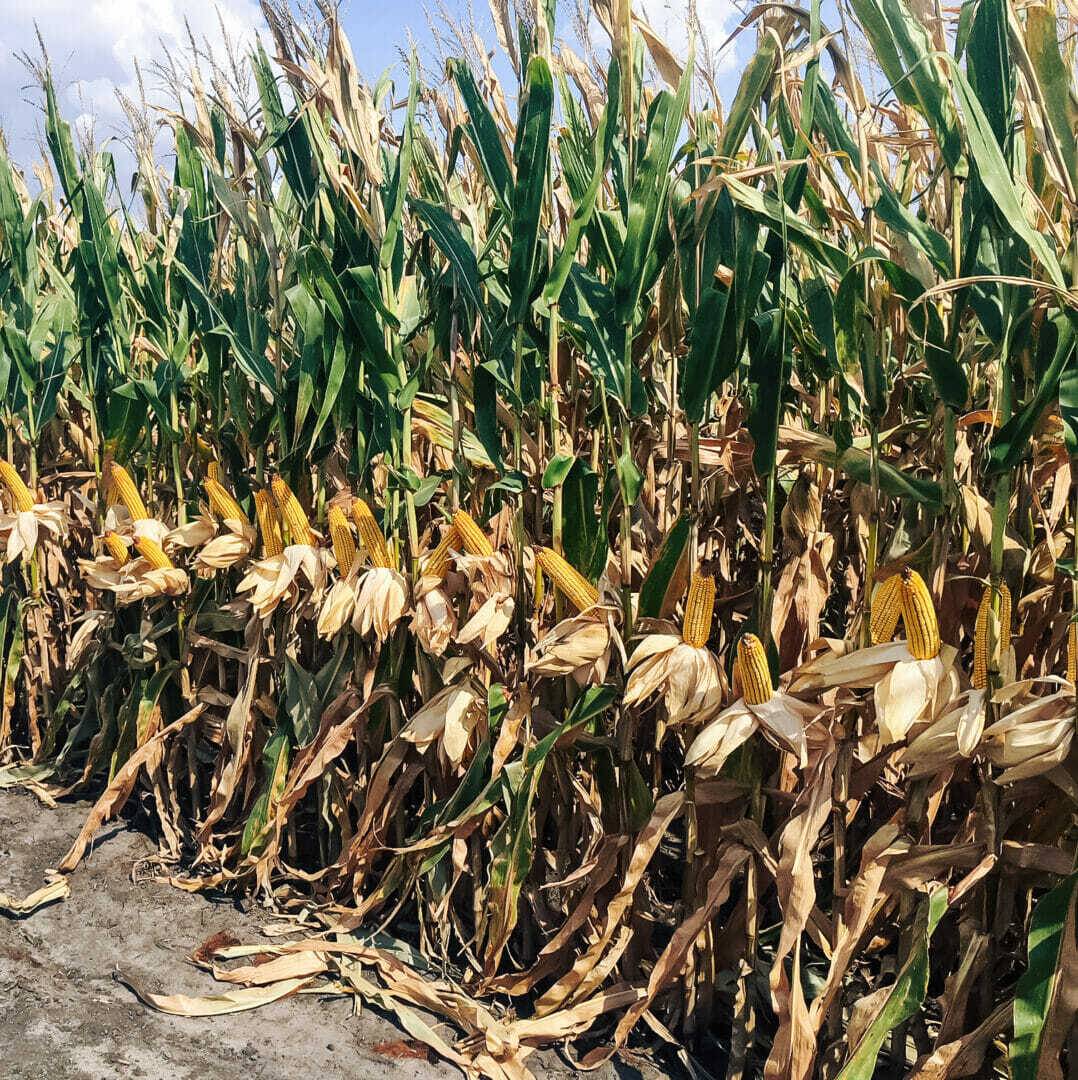
 As Harvest 2021 gets underway, we will start our morning checks to see which fields should be prioritized for harvest. Hybrid maturity helps guide us to certain fields, but sometimes a field stands out for another reason like late-season stalk lodging.
As Harvest 2021 gets underway, we will start our morning checks to see which fields should be prioritized for harvest. Hybrid maturity helps guide us to certain fields, but sometimes a field stands out for another reason like late-season stalk lodging.
Hybrids have different susceptibility to stalk rots as the season progresses. Knowing the hybrid you have on every field – and how each hybrid handles stalk rot diseases – is important. Another consideration is whether the hybrid you planted is a racehorse because racehorse hybrids do whatever it takes to fill an ear even if that means cannibalizing the stalk. This can be an unfortunate reality in a year like 2021 where moisture was very limited across most of Latham Country. A fungicide can keep the lower stalk healthier later into harvest, so if you choose to spray, you likely will see better standability.
Decisions made early in the season also influence late-season stalk health. Planter singulation is key. Doubles or multiples causes corn plants to grow on top of one another, so most of the time only one of those plants will develop an ear. Shallow planting depth causes the “crown” to establish closer to the soil surface, predisposing plants to root rot during this point in the season. Uniform competition is really important for neighboring corn plants, so that’s why good singulation and even emergence are important.
Planting population can influence stalk diameter and stalk health. You can push planting populations more if you keep your fertility levels in check. If you’re having stalk lodging issues and tend to push higher populations, then test soils and investigate where you may have an issue. If you notice foliar symptoms as you’re scouting throughout the season, then there is no better time than right after harvest to take soil samples. Potassium is a key nutrient for building healthy stalks. Micro-nutrients are also important, but it requires a balance. Too much of one nutrient can prevent other nutrients from being taken up by the corn plant.
As you walk your fields prior to fall harvest, do the “pinch” or “push” test to monitor stalk health. If you’re wondering about whether your soil fertility is influencing stalk health or haven’t soil tested in a while, feel free to give me a call. I’ll be glad to talk with you about the benefits of using Latham’s Data Forward® program.
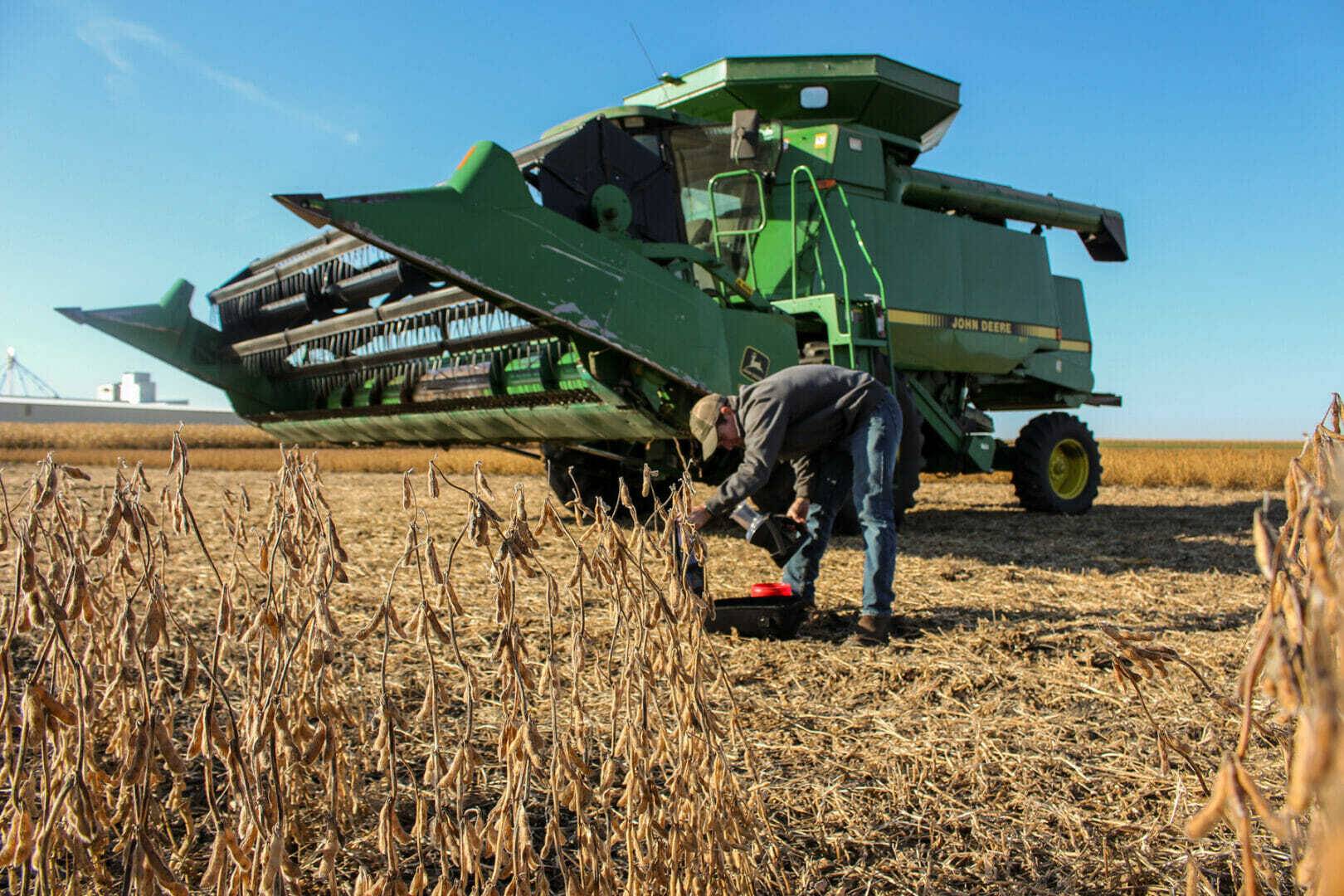
 I’m very hopeful that – even with the dry weather – our production fields can achieve an overall average year for production with sufficient seed for soybean sales in 2022.
I’m very hopeful that – even with the dry weather – our production fields can achieve an overall average year for production with sufficient seed for soybean sales in 2022.
Most soybean farmers’ biggest concern across Latham Country has been lack of moisture. Many have noticed aborted flowers, dropped pods, and restricted pod fill. Thankfully, our production fields in South Central Minnesota received a nice two-inch rain during the first week of August. Most of the growers in our area around Alexander, Iowa, got a nice one- or two-inch rain on August 20-21. That rain will help those fields fill out pretty well. Some of our fields in northern Minnesota also got a nice inch or more that weekend.
Rainfall has been extremely variable throughout the summer. On August 20, the Des Moines airport reported no rain but most cities throughout the metro got about 1.5 inches! “Spotty” rains have been the norm rather than the exception this season.
Besides the drought, infestations of two-spotted spider mites are popping up almost everywhere across Latham Country. This is common in periods of dry weather. Most growers seem to be willing to apply pesticides for control, especially when the market price for soybeans is high. Farmers in a few areas have reported Bean Leaf Beetles and Soybean Aphids at very low levels, so insecticide applications have not been necessary. Grasshoppers also flourish in dry conditions, and I have heard of farmers spraying to control this pest.
On the disease side, I’ve seen and heard of Sudden Death Syndrome (SDS) and White Mold this season. Dry weather usually hinders huge outbreaks of diseases, but it’s not unexpected that some areas will see things like this. Remember, SDS CANNOT be controlled with a foliar application of fungicide but there are some that can help on White Mold. I’ve also seen some Frogeye Leaf Spot (FLS) in a few fields but not enough to warrant a fungicide except in Southeast Iowa. I’m hearing about and seeing FLS in regions further north than usual, which is evidence this disease is moving farther north every year.
Call the Latham Team if you need help to diagnose situations or to recommend solutions. Be sure to keep field notes from these problem areas because that will be useful when you select seed in the future.

Join us for Latham Field Day LIVE!
Like all farm families, we know what it feels like to win big. We also know the agony of defeat. We watched helplessly, like so many of you during the last week of August, as winds reaching 92 miles per hour wreaked havoc across the Upper Midwest. When the skies cleared, we saw that our brand NEW Premier Agronomy Center had taken a terrific beating. Which was so unfortunate for our traditional live-on-the-farm Field Day.
The spirit of agriculture and America’s farmers is strong. Thankfully, technology allows us to share some of those research highlights with you. The program lineup includes our premier agronomy center, discussion on what we are seeing around the Midwest and new technologies and how to best use them.

What gives you a competitive edge?
There are many clever practices that can give athletes an edge. When drug testing became a standard, athletes had to discover legal ways to get an edge. It was noted that athletes who trained at higher elevations tended to perform better. As science progressed, they discovered the oxygen concentration is less at high elevations. Over a long period of time, our bodies will release a hormone to stimulate the production of more red blood cells because red blood cells carry oxygen in the blood. When the athletes returned to lower elevations to perform, they had more capacity to perform because they had significantly more red blood cells.
 How in the world does this relate to alfalfa? Think of the seed as an athlete of the acre, competing to germinate quickly and yield more. When we add AlfaShield seed treatment, the alfalfa seed has a performance-enhancing advantage. AlfaShield provides a distinctive winning edge as it combines a list of highly researched ingredients and incorporates them into an osmotic protective type coat.
How in the world does this relate to alfalfa? Think of the seed as an athlete of the acre, competing to germinate quickly and yield more. When we add AlfaShield seed treatment, the alfalfa seed has a performance-enhancing advantage. AlfaShield provides a distinctive winning edge as it combines a list of highly researched ingredients and incorporates them into an osmotic protective type coat.
Think of AlfaShield as wrapping your alfalfa seed in a sponge. It helps protect the fragile germ of the seed. It also helps draw moisture to the seed, which is particularly important when seeding into moisture-stressed soils. Summers-seeded alfalfa is up against the time clock to get four to six weeks of significant growth to develop the crown. That’s why it’s so important for the seed to germinate quickly. If there isn’t any rain, this delay could be costly. You’ll see in the 2022 Latham® product guide that we have added a dry matter (DM) ton advantage of AlfalfaShield compared to the old industry standard. AlfaShield has a bigger advantage in moisture-stressed soils.
We had scheduled alfalfa research trials, including seed treatments, for 2021. Unfortunately, this has been delayed because the university was unable to run it due to Covid-19. Because I already had the seed, I did a quick home study. All the seed came from the same lot: raw seed, old industry-standard treatment, and AlfaShield. I got three flower pots and used regular potting soil for consistency. Then I counted 100 seeds of each.
Note that in the first 65 hours, AlfaShield had ten times more seeds emerge than the other two treatments! Seeds with the other two treatments eventually emerged because this was an ideal situation. However, a farm field is not ideal. We know Mother Nature can be brutal, and the risk to the seed is high. AlfaShield is a tough seed treatment. It helps manage the risk of the acre better than the rest, and it shows up in the yield and quality. Emerge fast. Grow strong. Yield more!