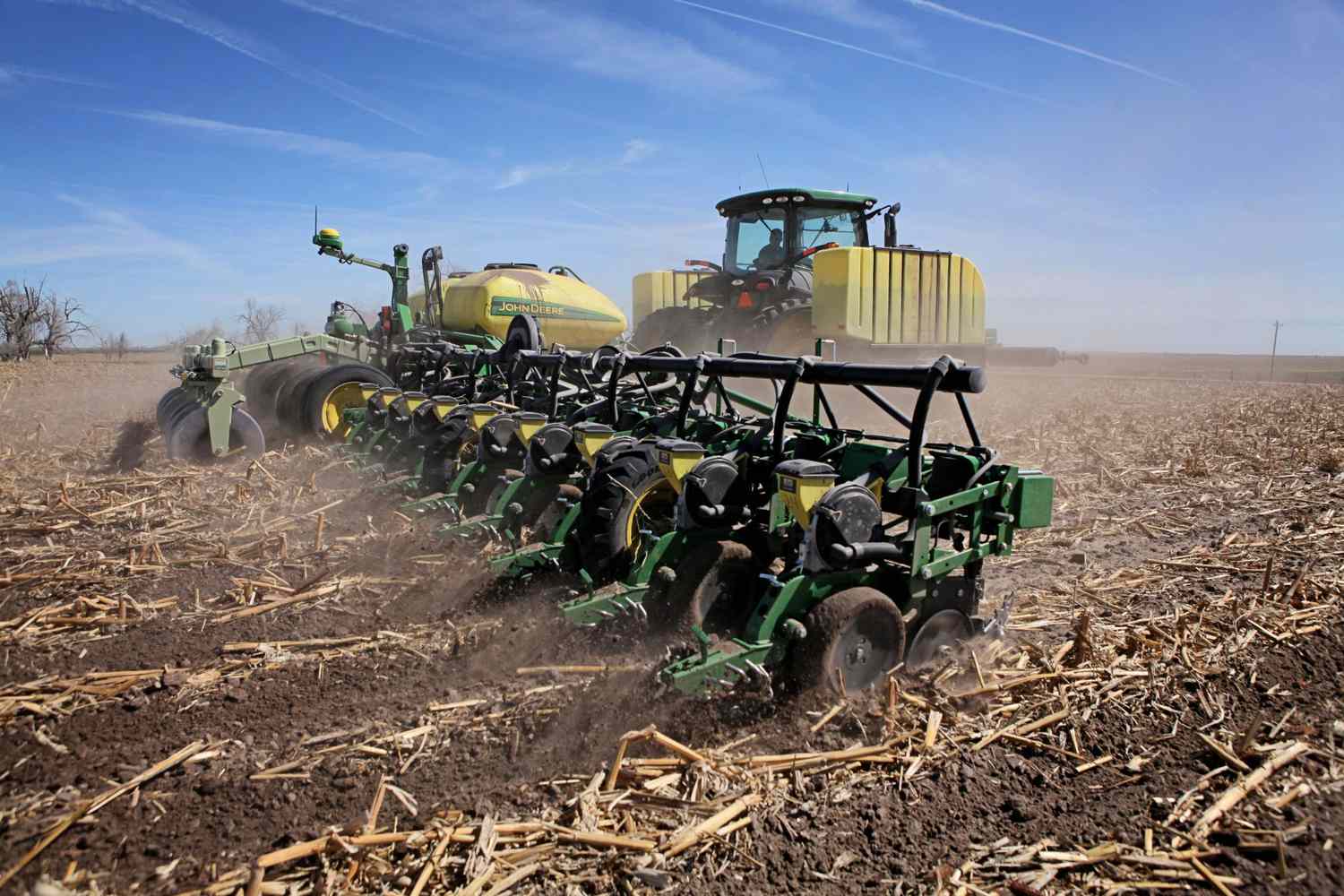
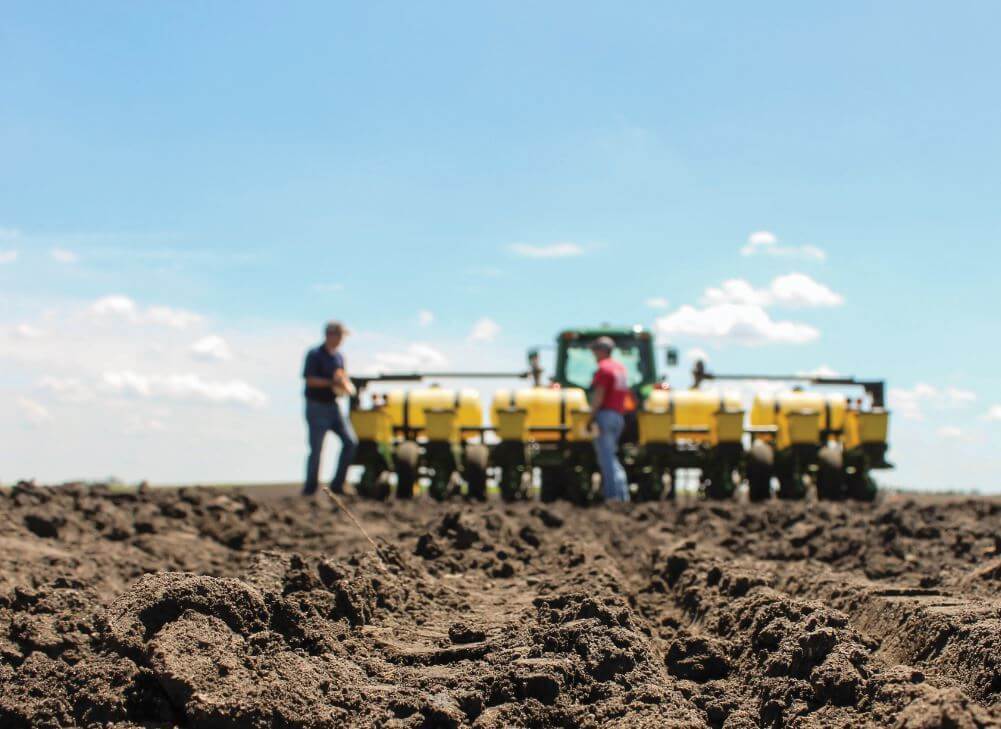
It’s hard to believe that spring is right around the corner, and planters will be rolling in two months’ time. There are many questions to consider before that first seed goes in the ground. Let’s take a closer look at three of them:
- How early is too early?
- Is the soil temperature warm enough to start planting?
- What depth should I be planting?
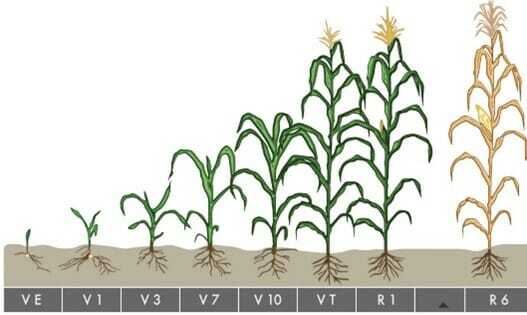
Q1: Generally, farmers maximize corn yield when they plant in late April or early May.
This holds true IF conditions are fit for planting. A mid-April planting date produces similar yield if young plants are not damaged by a freeze in May. In years with few growing degree days in late April and the first half of May, farmers can maximize corn yield when planting in mid-May.
When spring arrives early, farmers should weigh the risks and benefits of planting earlier than usual. Farmers with federal crop insurance will lose replant coverage if they plant before the earliest allowable planting dates specified by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) Risk Management Agency — even if they must replant due to factors other than freeze damage or poor emergence.
Seed treatments and planting high quality seed are a must with early planting.
Q2: Before planting, check the weather forecast and soil temperatures for your area.
It’s wise to check the soil temperature early in the morning of each field that you intend to plant. Wet soils and fields with more crop residue tend to have lower soil temperatures relative to drier soils or fields with less crop residue. Check the seed tag or talk to your seed dealer about the cold tolerance of your corn hybrids. Be aware that hybrids vary in cold tolerance.
Certainly, plant hybrids that have more tolerance for colder temperatures first. However, be aware that “imbibitional chilling” is a physical phenomenon that can override genetics. Imbibitional water uptake occurs within the first 48 hours after a seed is planted.
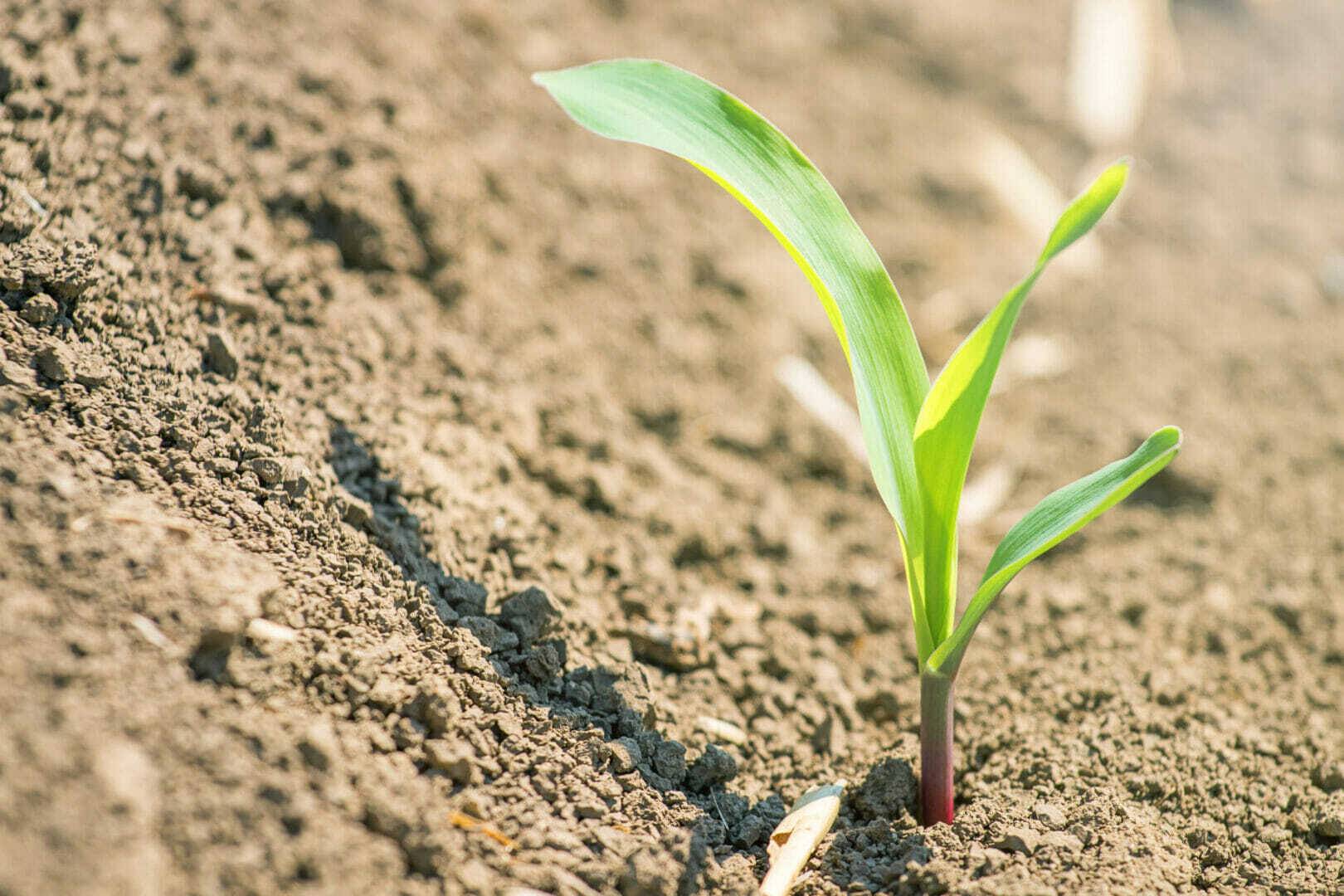
Once planted, corn seeds need a two-day (48-hour) window when the soil temperature at planting depth does not drop much below 50°F. When soil temperatures drop much lower than 50°F within that 48-hour time frame, chilling injury may affect seed germination and subsequent seedling growth.
During the osmotic phase of water uptake, which starts about 48 hours after the initial imbibitional phase of water uptake ends, the risk of chilling injury approaches zero. Thereafter, temperatures below 50°F can slow germination and delay seedling emergence. This can result in a longer exposure to soil-borne pathogens, particularly in soggy wet soils. If you expect the latter, use fungicide seed treatment for at least your earliest planted corn fields.
When corn seeds imbibe (take up) water, cell membranes stretch and cells expand. When a damaged cell membrane rehydrates, it may not return to its normal shape and size. This can create a “leaky” cell. Water is at its densest at about 39°F, so when cold water is imbibed additional membrane damage occurs. These ruptured membranes may occur in the cell walls and in the mitochondria. In the plant, this action may disrupt the embryo/endosperm enzymatic conversion to energy. It likely interferes with the emerging seedling’s development and reduces the plant’s growth rate.
- Debate exists about what specific temperature and timing causes imbibitional chilling. However, corn seeds that imbibe cold water (in the low 40s) in the first 48 hours after planting undoubtedly are affected.
- Planting when soil temperatures are above 50°F — and are not anticipated to drop much below this during the following 48 hours — alleviates concerns of imbibitional chilling affecting corn emergence.
Q3: Check seed depth and seed depth consistency across your planter units.
The “set it and forget it” approach to seed depth isn’t the best idea. To get corn off to the best start, it is important to achieve both rapid and consistent emergence following planting.

One aspect of achieving rapid and consistent plant emergence is by choosing the correct seeding depth and ensuring there is adequate and uniform moisture at the chosen seeding depth. The most common seeding depths recommended for corn range between 2.0 and 2.5 inches deep, and these planting depths can work very well within most conditions. However, certain soil moisture conditions at planting may warrant further examination/change in seeding depth.
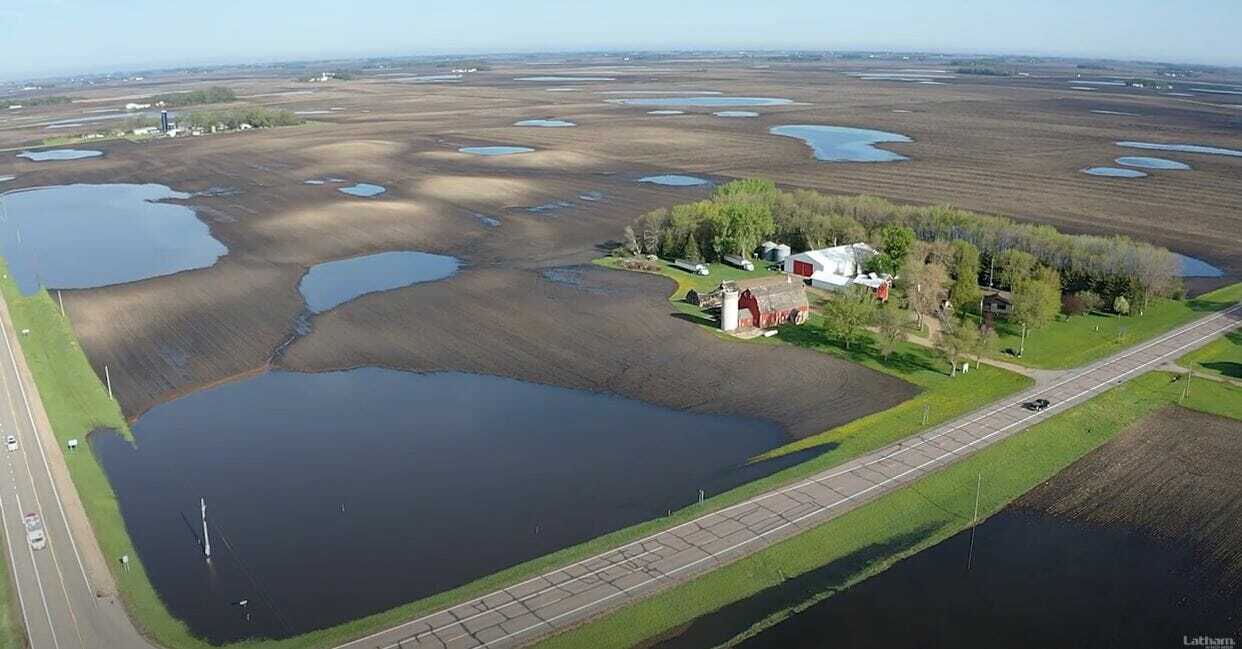
A corn seed imbibes soil moisture within the first 24 to 48 hours after planting, therefore maintaining both adequate and uniform moisture at seeding depth (not too wet and not too dry) within the first 48 hours is important. If the soil remains too dry, then the seed may be delayed in emergence until precipitation occurs. Furthermore, if the soil remains saturated after planting, the seed may rot and die.
Contact your local Latham® representative to find out more information about ideal planting depth for your area, or call 1.877.GO.LATHAM.