Take a look across Latham Country! We’re coming to you every week.
Latham Hi‑Tech Seed’s Corn Plot going in Northern Iowa!
Take a look across Latham Country! We’re coming to you every week.
Latham Hi‑Tech Seed’s Corn Plot going in Northern Iowa!
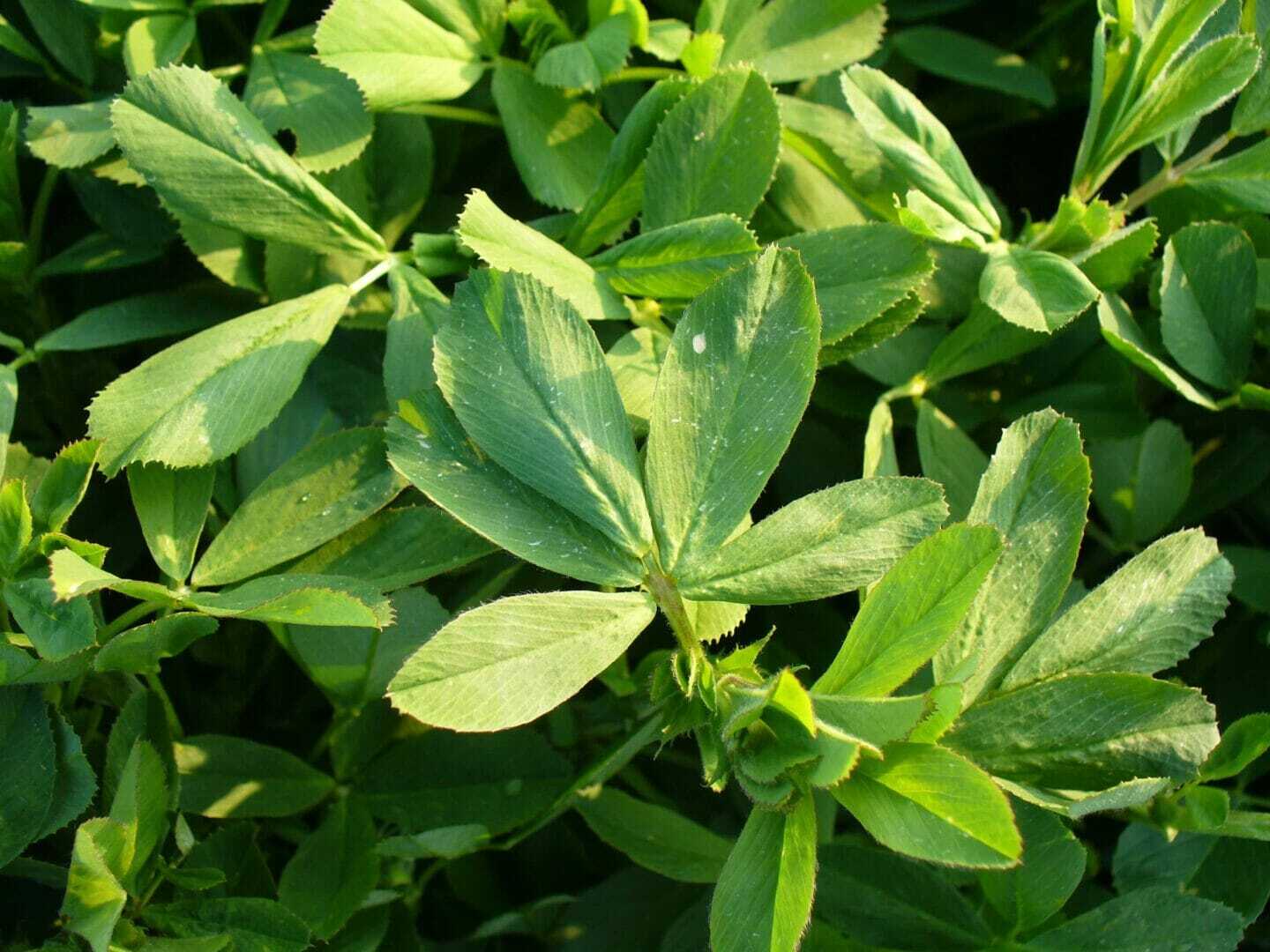

When it’s “go time,” you want to make sure that you have the best alfalfa to fit your field and your end use. Not all alfalfa is created equally, so it pays to give special attention to quality and yield.
Perform a soil test, so you know the soil’s pH, potassium and phosphorous levels. Sulfur and boron levels also factor into forage quality and yield. Alfalfa thrives in well-drained soils with a pH between 6.2 and 7.5. Avoid seeding alfalfa into soils that contain residual herbicides from a previous crop. Seeding alfalfa into existing alfalfa fields is discouraged.
Alfalfa seeding varies widely depending on your location. Seeding in the Upper Midwest can be done from mid-April through May. Seeding in June in the northernmost regions is not uncommon. Seeding early into soils that are too cold may result in delayed emergence, which can cause seedling rot and reduced stands. Planting too late may result in dry topsoil, which can also lead to reduced stands.
Precision planting is not just for corn and soybeans. Alfalfa should be seeded about three-eighths to one-half inch below the soil surface. The ideal stand establishment is between 30 and 35 plants per square foot.
Typical seeding rates for alfalfa seeded without a cover crop are between 12 to 15 pounds per acre. Alfalfa seedlings are very cold tolerant but cannot survive prolonged exposure to freezing temperatures.
High-quality seed is the best step you can take to ensure stand establishment! Look to your local Latham® dealer for help from the start.
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles (and delicious recipes) in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.

Too much of anything can be a bad thing. This week Phil Long explains how Calcium and Magnesium levels affect nutrients in your soil. (Which you should be testing, by the way.)

Phytophthora root and stem rot is a significant disease affecting soybeans across Latham Country. It can kill and damage seedlings and plants from planting almost through harvest. This disease especially favors saturated conditions early in the growing season.
You’re most likely to find Phytophthora in the following places:
Begin scouting as early as emergence where soils are saturated by heavy rains following planting. Where gaps in the row appear, carefully dig down to the seed zone. Infected seeds may rot before germination. Others may germinate but fail to make it to the surface.
In other instances, soybean plants may emerge from the soil and then die. These dying or dead plants often show a “pinching” of the stem just at or slightly below the soil line. This symptom is commonly referred to as damping-off.

If damping-off is a problem in the spring, watch for Phytophthora infection following rainy periods later in the season. The stem rot phase is easily recognizable by the presence of a distinct chocolate-brown lesion moving up the stem from the soil line. Initially, the upper stem of the plant may remain green. The plant will eventually wilt, turn yellow, and then die with leaves remaining attached.
The root rot phase of Phytophthora is not as readily recognized as the stem rot phase. Infected plants can be stunted and less vigorous, although this is hard to spot unless the infected plants are near a healthy comparison. A close inspection of the root system will reveal a significant reduction in the number of secondary roots and fine root hairs that help the plant take up moisture and nutrients. Plants with the root rot phase may mature a week or two earlier than healthy plants in the field.
Management
Many soybean varieties have resistance genes. The most common group of genes are known as Rps genes (“Resistant to Phytophthora sojae”). Varieties with “stacked” genes can show significantly higher resistance to Phytophthora. Specific information on PRR genes for each of Latham® soybean varieties is included in our 2023 Seed Guide.
Using Latham’s SoyShield® and SoyShield Plus seed treatments is a proven, effective way to protect against early-season diseases like Phytophthora. Using our seed treatment gives you the confidence and flexibility for a strong start to the growing season.
*Sources:
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles (and delicious recipes) in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.

It’s no secret that optimal yields result from a combination of many factors: environment, plant nutrition and nutrients to name a few.
 Plant nutrition is key to maximizing the yield potential of today’s plant genetics. To meet the intensive nutritional demands of these plants, there must be a higher fidelity to soil condition and nutrition. Removing nutrients removes nutrition from the soil reserves.
Plant nutrition is key to maximizing the yield potential of today’s plant genetics. To meet the intensive nutritional demands of these plants, there must be a higher fidelity to soil condition and nutrition. Removing nutrients removes nutrition from the soil reserves.
There is a no “one-size-fits-all” nutrition program, and there are many variations of soils and environments. So customizing nutrition programs by field can help optimize yield. Today’s technology allows us to do just that!
Many years ago, we heard about a farmer who found a unique combination of cover crops that worked well for his soils and climate. He tracked everything precisely and found that soil organic matter (OM) increases by 0.1% each year. This may not seem like much, but the impacts are exponential. In 10 years, you gain 1% more OM. For every 1% OM, the soil can hold 1 acre inch of rain. That’s 27,000 gallons of water.
This farmer is improving water and nutrient-holding capacity of the soil in the root zone. During drought years, his farm’s yield was only down 10 bushels while the average yield decrease was 60 bushels. Plus, his farm produced the same yields using less nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P) and potassium (K) because leaching is reduced.
Why not experiment on your own farm? Start small and see how you can capture more yield on the same acre. Here are a couple resources to help you get started:
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles (and delicious recipes) in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.
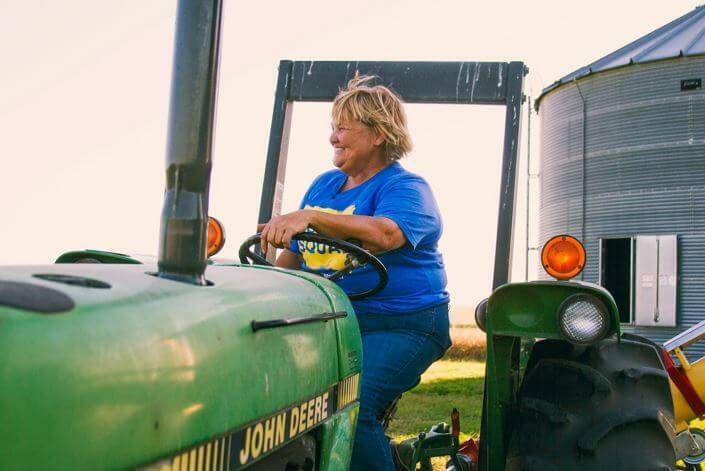

 When it comes to farming — specifically as a FarmHer — April Hemmes’ resume speaks for itself.
When it comes to farming — specifically as a FarmHer — April Hemmes’ resume speaks for itself.
Besides earning her Animal Science degree from Iowa State University, April has served in leadership roles for the United Soybean Board, USDA Foreign Ag Service Technical Advisory Council and the U.N. Food Security Summit . . . just to name a few. She’s been described as a trailblazer for women in ag — a reference she humbly dismisses and appreciates at the same time.
“I really don’t think you are a trailblazer if you are just doing what you love and pursuing your dream,” April says. “I hope the fact that I farm gives other young women hope that someday they may be able to go home and work on their family farm and manage it, too!”
April lives on the farm her great grandfather bought in 1901. It was always a diverse operation, so when she came home to farm, April knew she could have hogs too. They cleaned out an old building and turned it into a farrowing house with raised crates that April bought from a nearby producer who’d gone out of business. She bought 30 gilts, started a farrow-to-finish operation and farmed with her grandpa and her dad.

When the market went to 9 cents a pound in the late 1990’s, April retreated from the hog business to focus more on the 60-head cow calf herd she had purchased from her dad by then.
“I really liked having hogs around,” April says. “But something had to go.”
Business decisions like that helped propel April into a lifetime of farming that has captured headlines as “Midwest Farm Mom of the Year” and on the cover of “Successful Farming” magazine. Her husband, Tom Kazmerzak, always has worked in town and not on the farm. April has been the owner and operator of her family’s century farm south of Hampton, Iowa for more than 40 years, raising corn, soybean and pasture land.
“Farming has always been what I wanted to do with my life,” April says. “I always helped on the farm and knew education and experience would be the best way to be ready for the challenge.”
One of April’s secrets to success is getting up early to answer emails so other farmers feel heard.
“The most gratifying thing I hear is when another farmer thanks me for what I am doing,” she says. “It really means a lot to me.”
The other secret to her success? Sheer stubbornness.
“I did not have a father who encouraged me to farm, but I was always expected to do everything on the farm,” April says. “I’m very proud to carry on the tradition of farming. It’s my love, my life and my legacy.”
Enjoy April’s favorite cookie recipe below.
Did you enjoy this video? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles, videos (and delicious recipes) in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.

 Weather concerns are top of mind as farmers across Latham Country look ahead to spring 2023 planting. Customers frequently ask us how to mitigate risk from the 2022 wet planting season.
Weather concerns are top of mind as farmers across Latham Country look ahead to spring 2023 planting. Customers frequently ask us how to mitigate risk from the 2022 wet planting season.
While we want to maximize the yield potential of early planting, 2022 data shows us that delayed planting can result in very good yields — and better yields than planting when conditions are unfit.
Consider these factors to successfully mitigate potential risks of delayed planting:
We suggest staying with a hybrid selection plan that does not vary significantly from previous years. A couple management changes at planting time to get your crop off to a great start will result in more success than totally changing your hybrid selection.
Remember, most corn yield is created in July and August. Get your plants off to the best start, so they can take advantage of that part of the growing season. Don’t get discouraged if you encounter a bit of a delay. Stick to the hybrids in your original plan through the end of May.
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles (and delicious recipes) in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.


One reason Latham Hi‑Tech Seeds opened its Premier Agronomy Center on the Latham family’s Iowa Century farm was to collect data using real-world practices and to research solutions for real-world problems. More farmers are interested in biologicals to reduce fertilizer and other input costs and/or to build soil health.
A biological product, or biofertilizer, contains living microorganisms that promote fertilizer efficiency or plant growth. Most of these products are naturally occurring in the environment but likely do not occur in high amounts in your field.
At Latham’s Premier Agronomy Center in 2022, we used Pivot Bio PROVEN® and Azotic Envita® on corn. Both nitrogen-producing bacteria products were trialed on a large scale and applied in-furrow with LH 5245 VT2 PRO RIB. PROVEN yielded 213.1 bushels per acre (bu/A), and Envita yielded 208.1 bu/A while the untreated LH 5245 yielded 206.2 bu/A. (Also please note that I applied about 40 lbs per acre less nitrogen on all the biological products, so I saved about $20 to $30 per acre when accounting for the product cost.) We have seen similar past results with PROVEN on our farm despite the dry conditions we have had. Envita also may be sprayed over the crop in-season — a process that our team will try in 2023.
Another biological/foliar product that I’ve used on my own farm for soybeans is BW Advance from BW Fusion. This product has foliar nutrients plus biologicals. When applied around soybean reproduction time, it can help reduce flower and pod abortion plus reduce moisture loss during drought stress. It takes about a 1.5 bu/A yield increase to pay for the product at current soybean prices. In 2022, I saw an average of 2.3 bu/A advantage. Keep in mind, 2022 was very dry and this particular field has some underlying fertility issues.
If you are going to try biologicals, you must take care of pH and other soil fertility deficiencies. The microbes in your soil, especially bacteria and fungi, thrive based on proper pH and physical soil environment. For example, if you have a pH of 5.0 or heavily compacted soils, you’re not going to see a boost in soil life until you correct those issues.
This year I used two foliar/soil-applied products, Midwest Bio-Tech’s Chandler Soil and TerraMax’s Ag Soft. The goal of these products is for compaction alleviation and residue management. I’m using these products on our cover crop and no-till plots. During the next few years, I will share results and show any soil structure changes. We also use seed-applied products, including Talc U.S.A.’s Microsurge inoculant and Encompass, as well as TerraMax’s Vertex and Micro MX.
How will we know which products may benefit our farm the most? Our plan is to try them! I will share soil health tests and how they can aid us in continuing to decipher the complex world of biologicals.
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.


Agronomists often tout the merits of selecting hybrids to fit your soil types, but it’s also important to select hybrids that match your management style.
Latham Hi‑Tech Seeds’ Premier Agronomy Center provides opportunities for us to learn and share how Latham® products interact with the environment and perform under different management styles. In 2022, we adapted our stress wheel study to show how different Latham brand hybrids react to population differences. We planted 20 different Latham hybrids at both 24,000 and 36,000 plants per acre (ppa) to track how each hybrid adjusts its ear flex – or yield – to high- and low-competition environments.
Overall corn yield comes from three areas: (1) plants per acre; (2) ears per plant; and (3) weight per ear. If we look specifically at an individual corn plant, yield comes from these three areas: girth in the early season, length in mid-season and kernel depth in late season. The hybrid stress test helps us better understand how your favorite Latham hybrids adjust their yield in high- or low-stress environments, which in turn helps you better understand when to reduce stress for these hybrids.
For example, if a hybrid gets most of its yield from flex in girth, you should reduce early-season stress. Plant these hybrids in warm soils; provide fertility at the planter, and make sure nitrogen is in an available form early in the season. All hybrids determine girth based on how healthy or stressed the plants are from emergence to V7, so anything you can do to help them at that stage retains more yield.
The critical time for hybrids that flex in length is from V8 to R2. Making sure these hybrids are healthy in early summer is more important. Side-dress applications are beneficial to these hybrids.
The last group is those that flex in kernel depth, which occurs from R3 to R6 when the corn is filling its kernels, so nutrients move from leaves to the ear. These hybrids can benefit greatly from fungicide because it gives them extra time in the grain fill stage to add weight to the ear.
Although we always talk about hybrids flexing up for bigger yields, a corn plant thinks of it differently. It starts with very high expectations and then flexes down in each direction based on the stress it encounters during the season. Each hybrid’s genetics can vary by how much emphasis it puts on these three areas of yield.
We were intrigued by what we learned from our stress test in 2022 and look forward to learning more in 2023 about how our hybrids adjust their yield. Talk with your local Latham® rep to help you match our hybrids to your management style. Each local salesperson is supported by a team of seed specialists located across our six-state territory.
Did you enjoy this article? We want to (TECH)talk with you! Sign up for our newsletter to receive agronomy articles in your inbox! We’ll talk soon.